Btrust Builders
Schnorr and Steady Wins the Race: The Case for Batch Validation
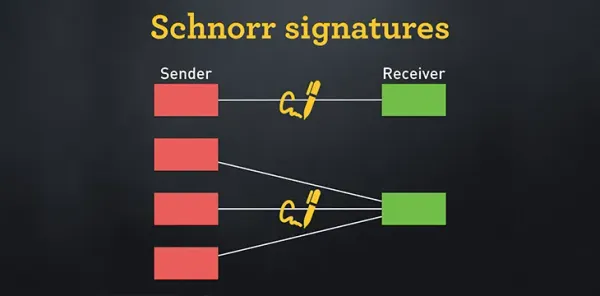
Understanding BIP340 Schnorr Signature Verification

Btrust Builders
Understanding BIP340 Schnorr Signature Verification
Btrust Builders
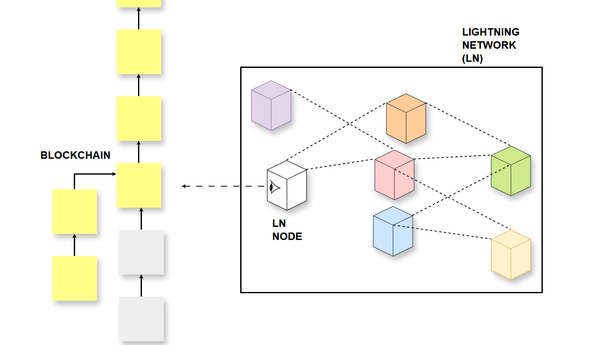
Exploring how Lightning Nodes source onchain data.

Btrust Builders
We take a closer look at the progress and architecture of the dual-funded channel implementation in the Lightning Development Kit (LDK).
Btrust Builders
Written by Sadiq Ismail In theory, Bitcoin Core’s block-building algorithm reserves 4,000 WU for miners’ coinbase transactions. This means it should generate a block template with a weight of 3,996,000 WU. However, in practice, this is not the case due to an accidental double-reservation bug (see

Btrust Builders
Written by Sadiq Ismail In our journey to understand Bitcoin's cryptography, we've already seen how the ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) plays a key role in securing transactions. But, as Abubakar Sadiq Ismail pointed out in his previous piece, ECDSA comes with a notable vulnerability;

Btrust Builders
Written by Sadiq Ismail Digital signatures are crucial for ensuring the authenticity and integrity of digital documents, offering a level of security that physical signatures simply can't match. Among the various digital signature algorithms available, the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) stands out for its efficiency and
Btrust Builders
Written by Collins Okafor A Bitcoin block is a fundamental component of the Bitcoin blockchain, acting as a container for a group of transactions. Each block is linked to the previous one, forming a secure chain of data. At the heart of each block is a block header, which includes
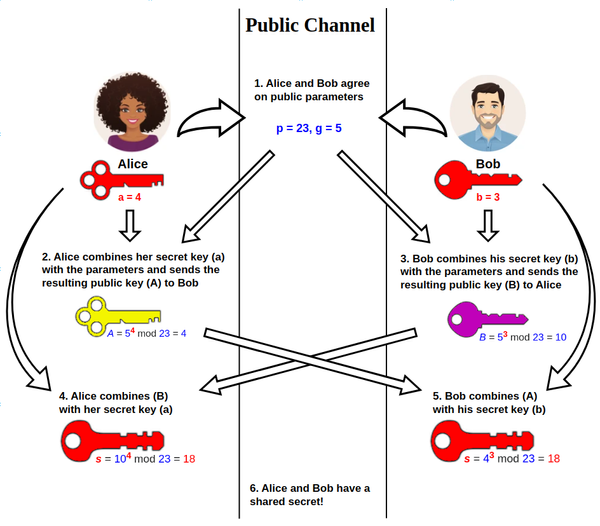
Btrust Builders
Written by Charles Chege Ecash, conceptualized by David Chaum in the 1980s, was one of the first attempts to create anonymous digital currency. Chaum's idea used cryptographic proofs to mint and manage electronic tokens, ensuring the privacy of transactions through blinded digital signatures. These early ideas laid the
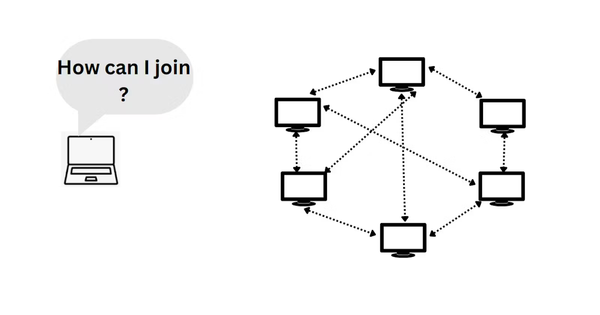
Btrust Builders
Written by Aurelia Naiyoma In the Bitcoin Network, peer discovery is an essential process that ensures nodes can effectively connect and exchange information. This plays a critical role in securing the network by ensuring blocks are propagated and transactions can be validated, forming the core basis of how the network

Btrust Builders
Written by Aurelia Naiyoma Imagine an instance where every tiny code change is traceable, and transactions are secured with unbreakable chains of verification. This is the power of Merkle trees, a deceptively simple data structure at the heart of systems like Git and Bitcoin. Merkle trees work by converting data

Btrust Builders
Written by Oghenovo Usiwoma Lightning is a second layer for Bitcoin that uses micropayment channels to scale the blockchain’s capability to conduct transactions more efficiently. This layer consists of multiple nodes that can open and close payment channels with each other, without having to broadcast every transaction to the

Btrust Builders
Written by Ibironke Marvellous The Lightning Network is a second-layer payment protocol built on the Bitcoin network. It is designed to improve the scalability of the Bitcoin network and provide near-instant, low-cost transactions. In contrast, the Bitcoin network is a first-layer payment protocol that supports secure, decentralized transactions. The Lightning